Location: Central Athens, near American Embassy and Athens Music Hall
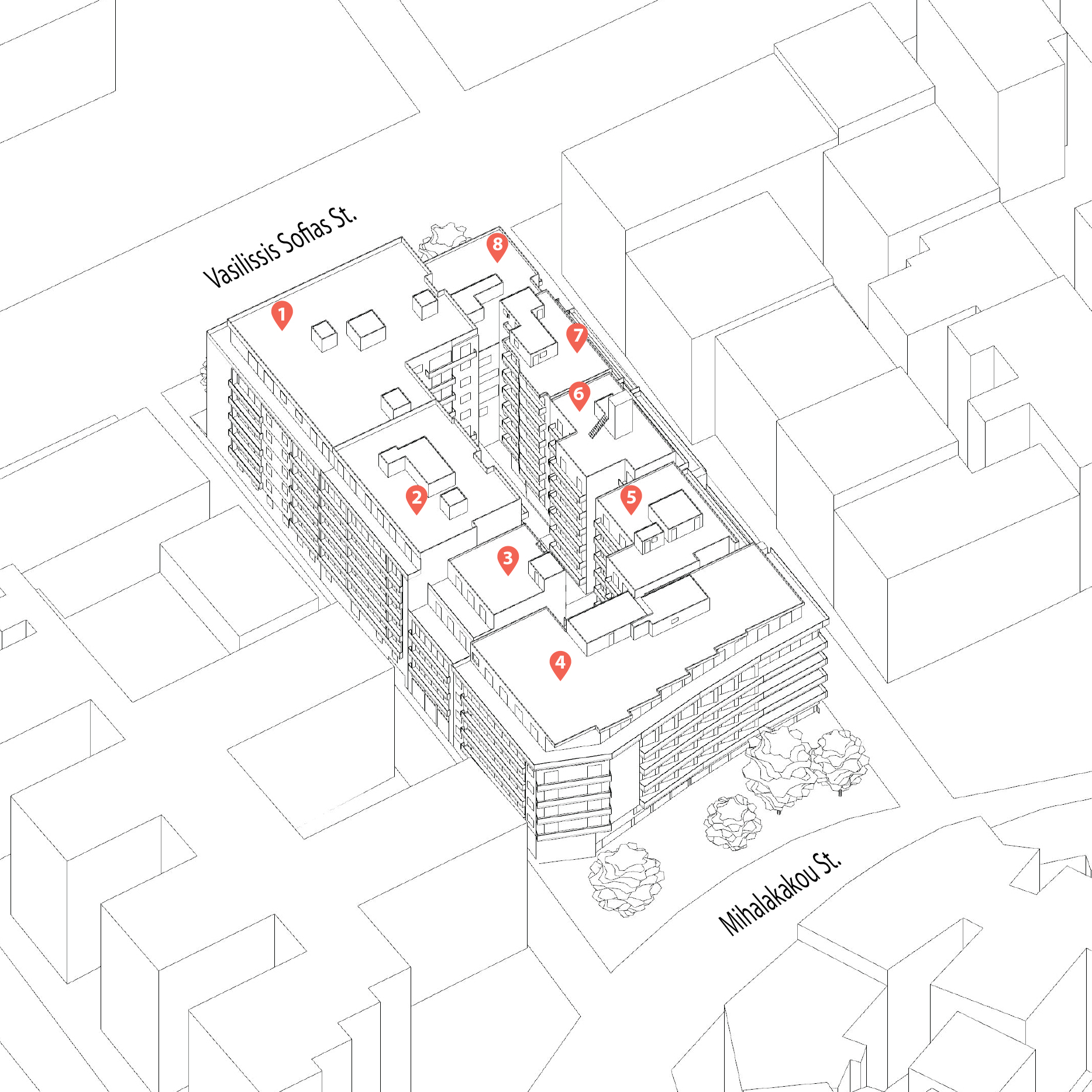
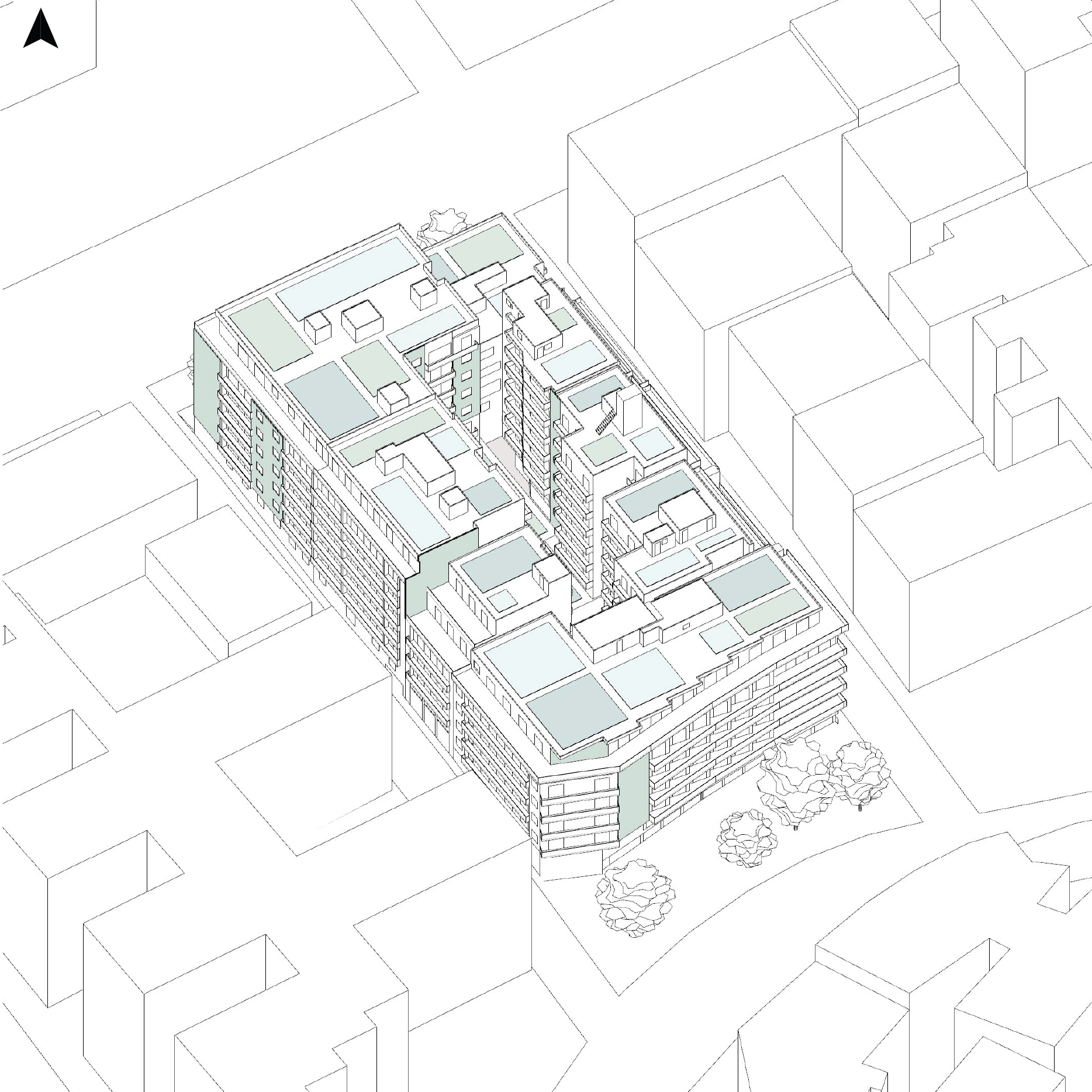
Context: Typical Greek urban block with flat-roofed buildings and an inner block void
Project Highlights:
- Created a detailed 3D model based on precise on-site measurements.
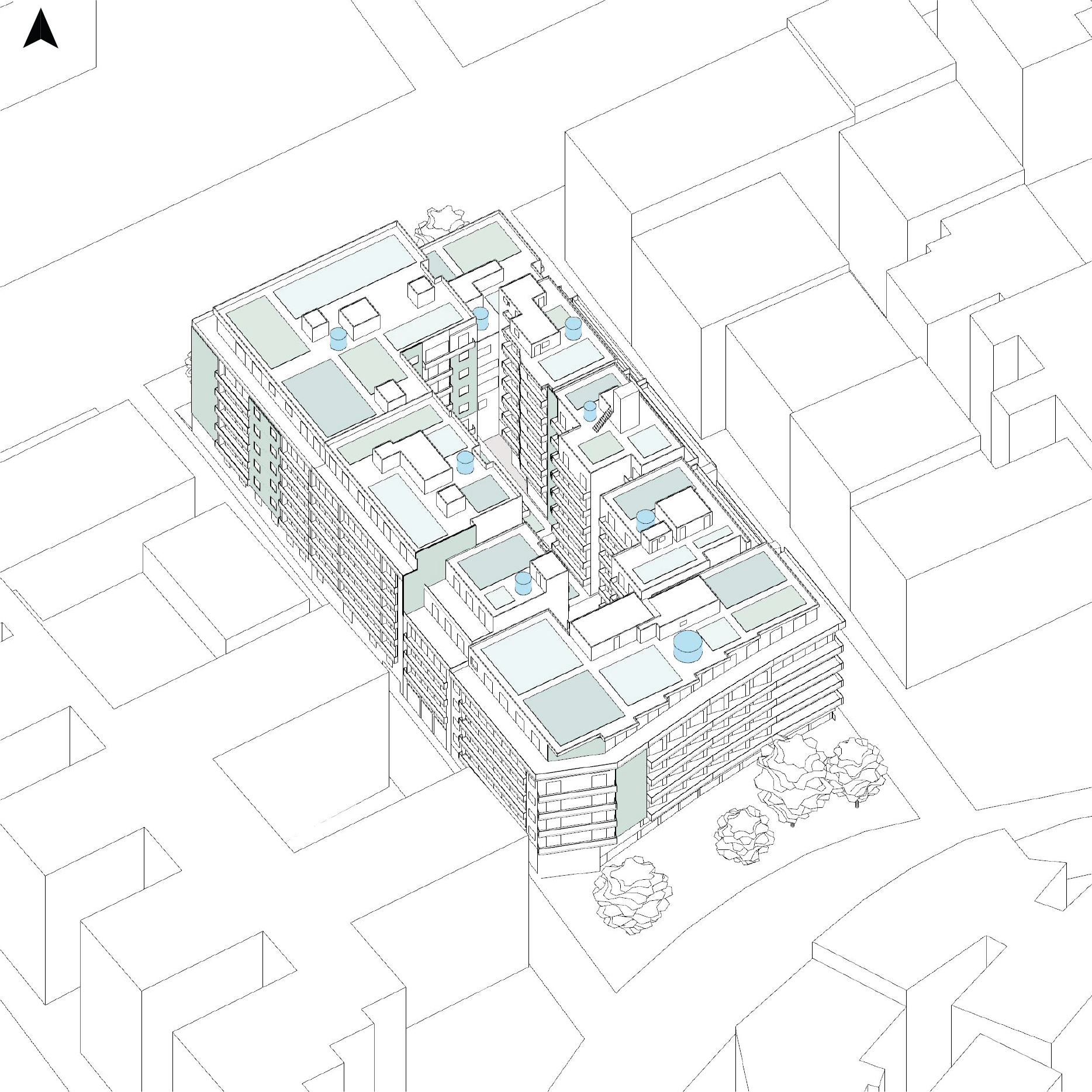
- Tested two scenarios:
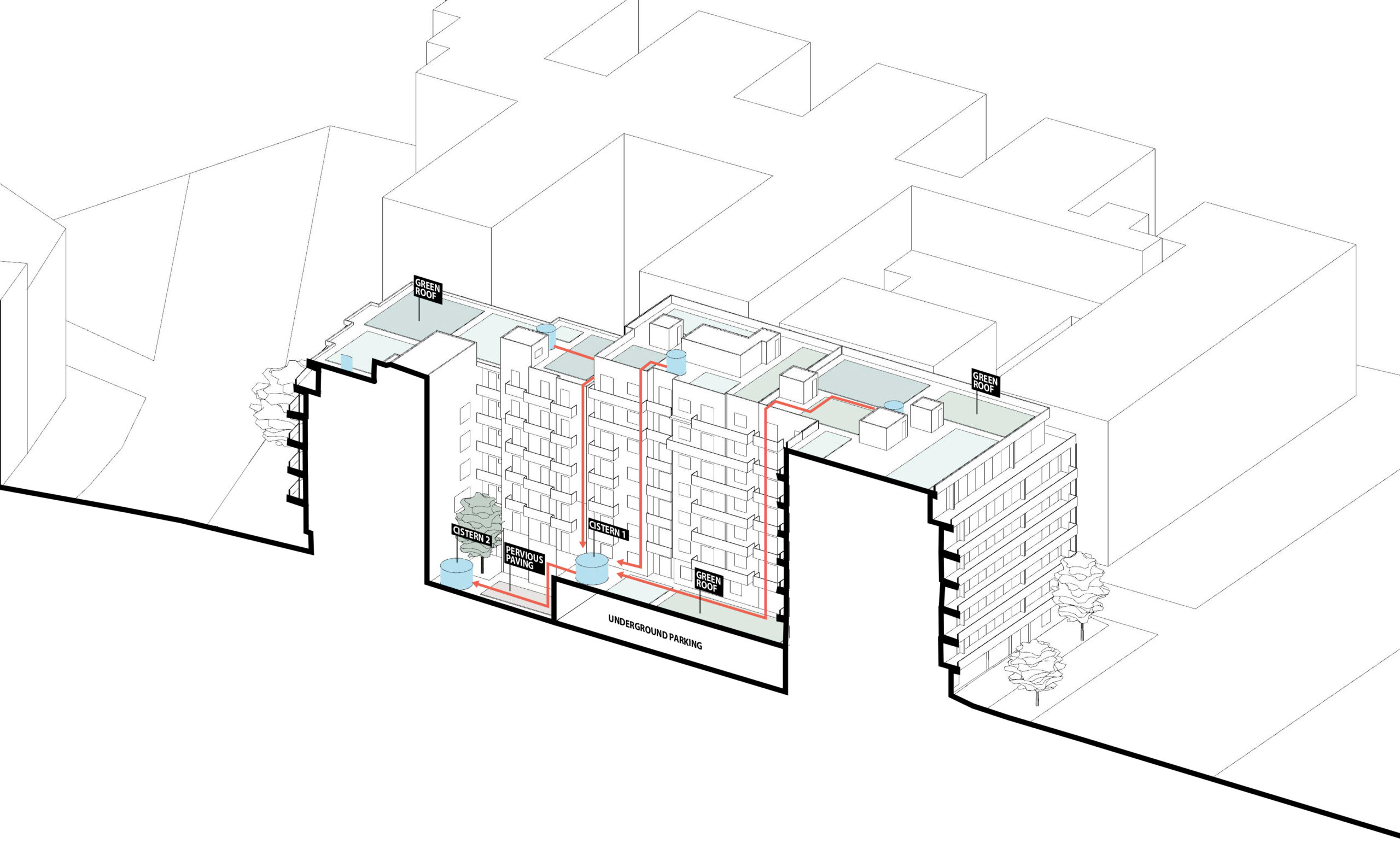
- Green infrastructure only (green roofs, living walls, permeable paving)
- Green infrastructure plus rainwater harvesting cisterns
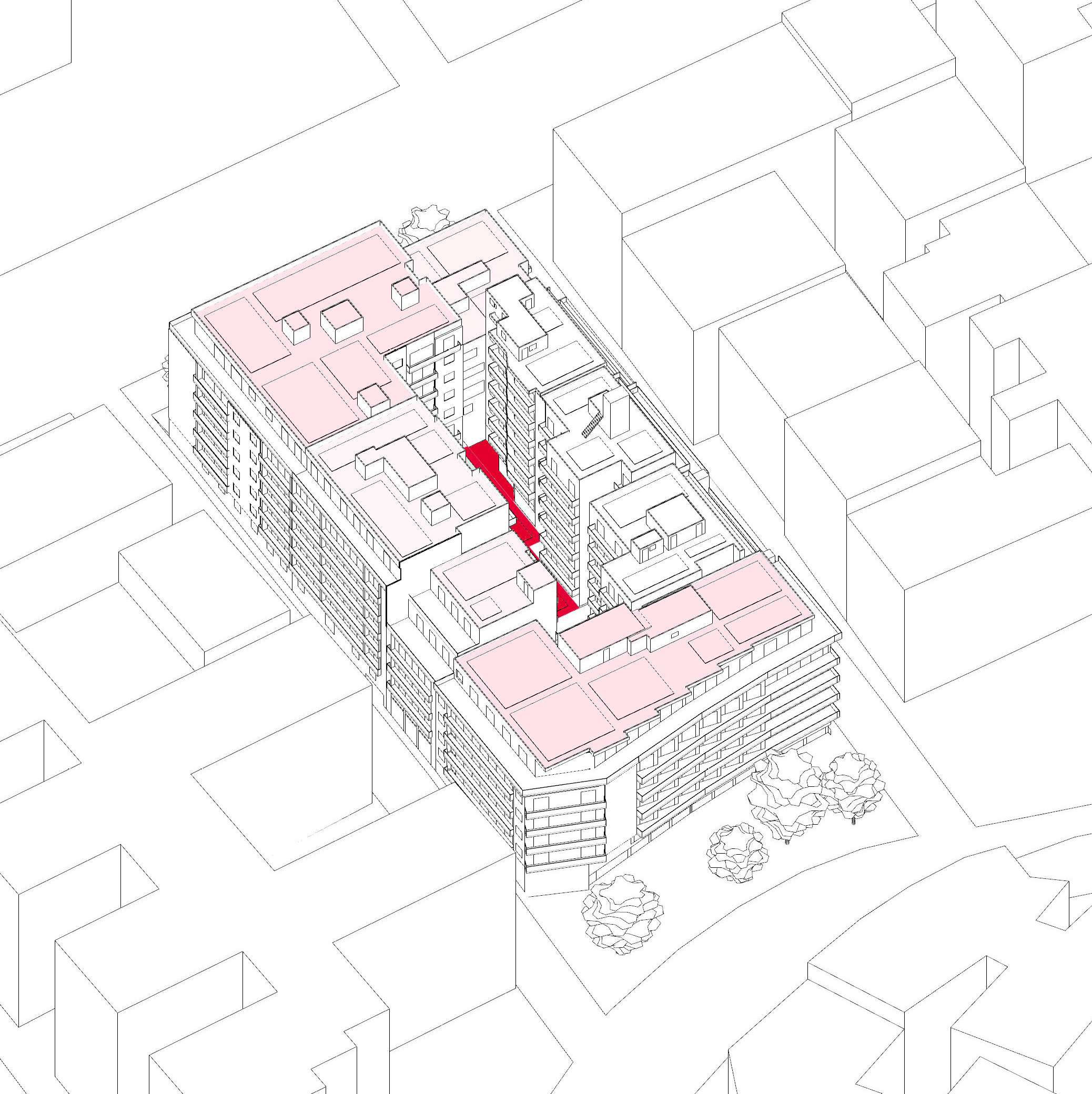
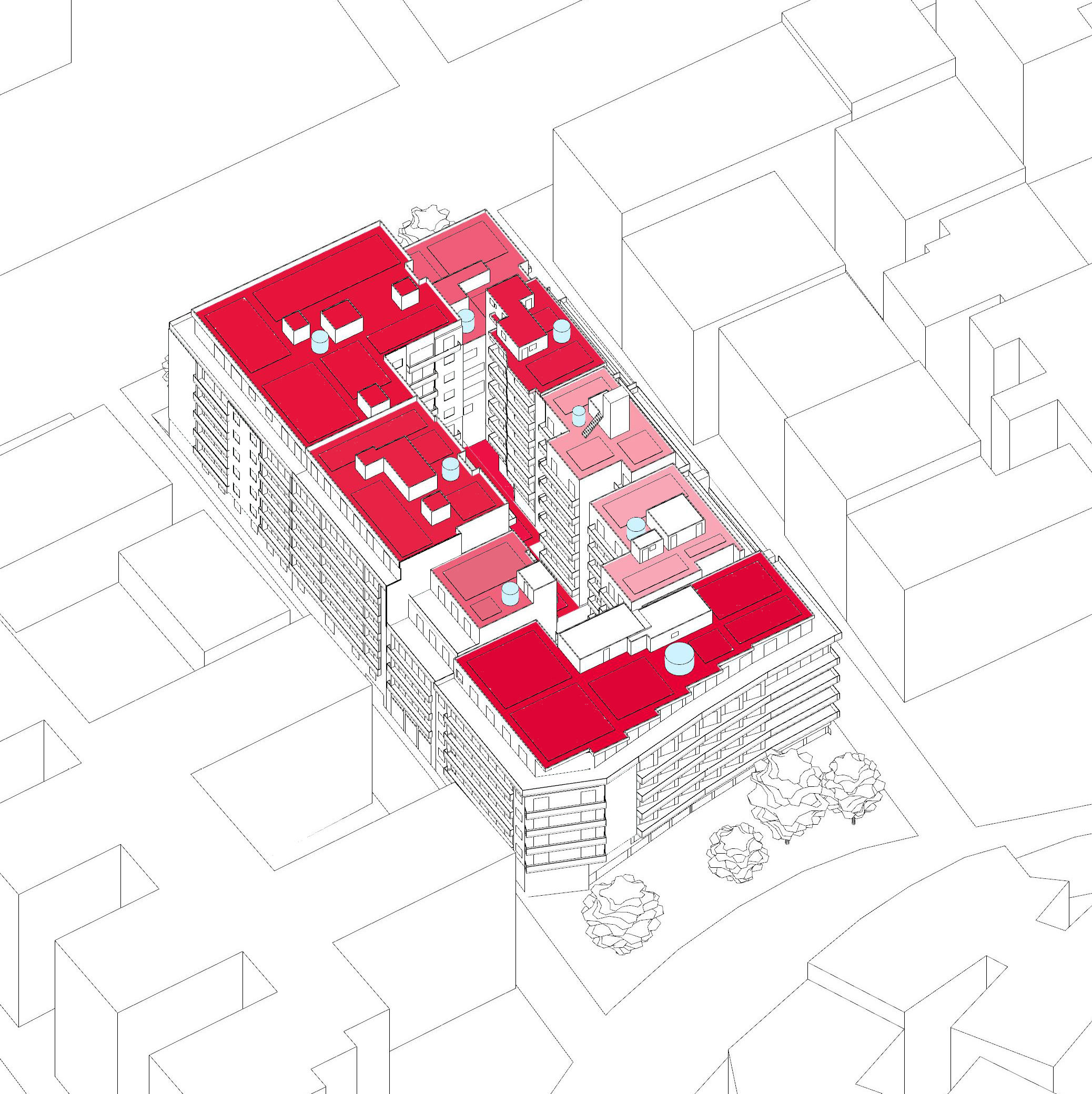
Simulation Results
- Runoff Reduction:
- Scenario 1 (no cisterns): 15-30% runoff reduction on rooftops; 77% in inner block void
- Scenario 2 (with cisterns): 62-86% rooftop runoff reduction; up to 85% in inner block void
- Irrigation Sources:
- Scenario 1: Mostly network water supply; precipitation covers 5-9%
- Scenario 2: Significant use of stored rainwater (13-36% on rooftops) reducing network water dependency
- Seasonal Highlights:
- Summer: Scenario 2 achieves nearly 100% runoff capture; cisterns vital for irrigation during dry periods
- Autumn & Winter: Cisterns greatly reduce runoff and network water use, adapting to moderate rainfall
- Spring: Cisterns provide 15-79% of irrigation water, fueled by winter recharge
- Conclusion:
- Integrating rainwater harvesting with green infrastructure significantly boosts urban water sustainability and irrigation efficiency—offering a replicable model for cities facing water challenges.