UBWARMM
Storm water management modelling
for Greek urban blocks

This project has received funding from the Hellenic Foundation for Research and Innovation (H.F.R.I.) and the General Secretariat for Research and Technology (G.S.R.T.) [Project Number 4603].
UBWARMM is a cutting-edge research project focused on advancing Water Sensitive Urban Design (WSUD) strategies through architect-friendly, data-driven tools for sustainable rainwater management in urban environments. Funded by the Hellenic Foundation for Research and Innovation (H.F.R.I.), the project addresses the pressing need for resilient urban infrastructure in cities facing increasingly frequent extreme rainfall events and persistent heatwaves, particularly in warm and dry climates.
At the core of the UBWARMM project is the development of MARSH (Model for Assessment of Runoff and Stormwater Harvesting)—a comprehensive, 3D computational model designed specifically to support architects and urban designers in assessing and visualizing stormwater management scenarios. Implemented in the Grasshopper visual programming environment, MARSH allows users to create, evaluate, and compare the performance of various Best Management Practices (BMPs) in mitigating stormwater runoff and enhancing rainwater harvesting.
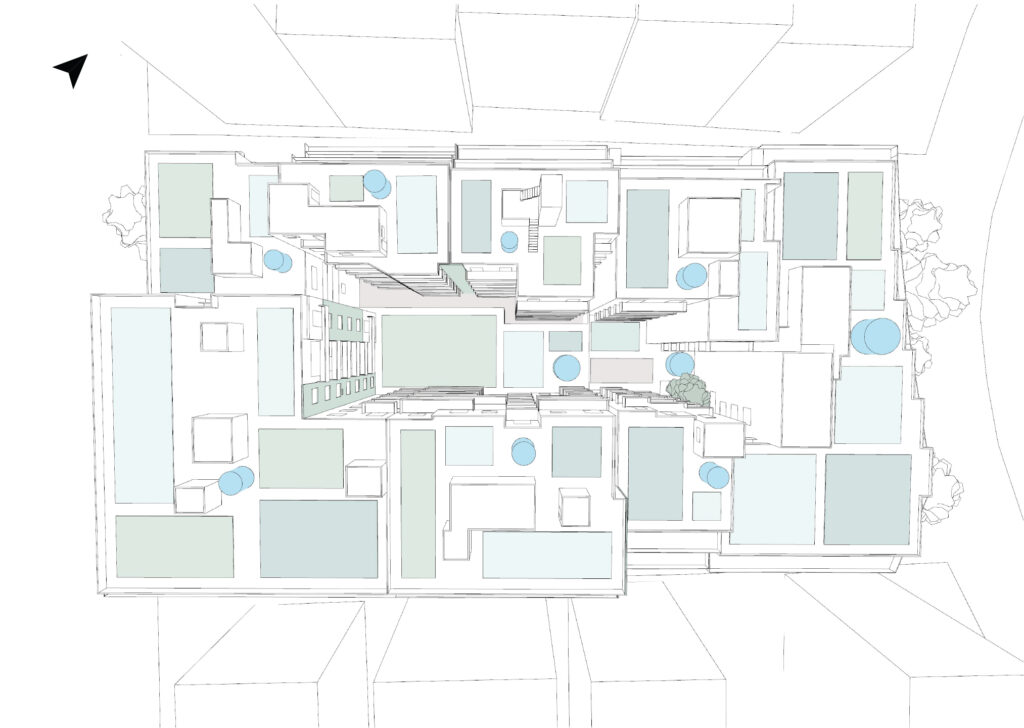
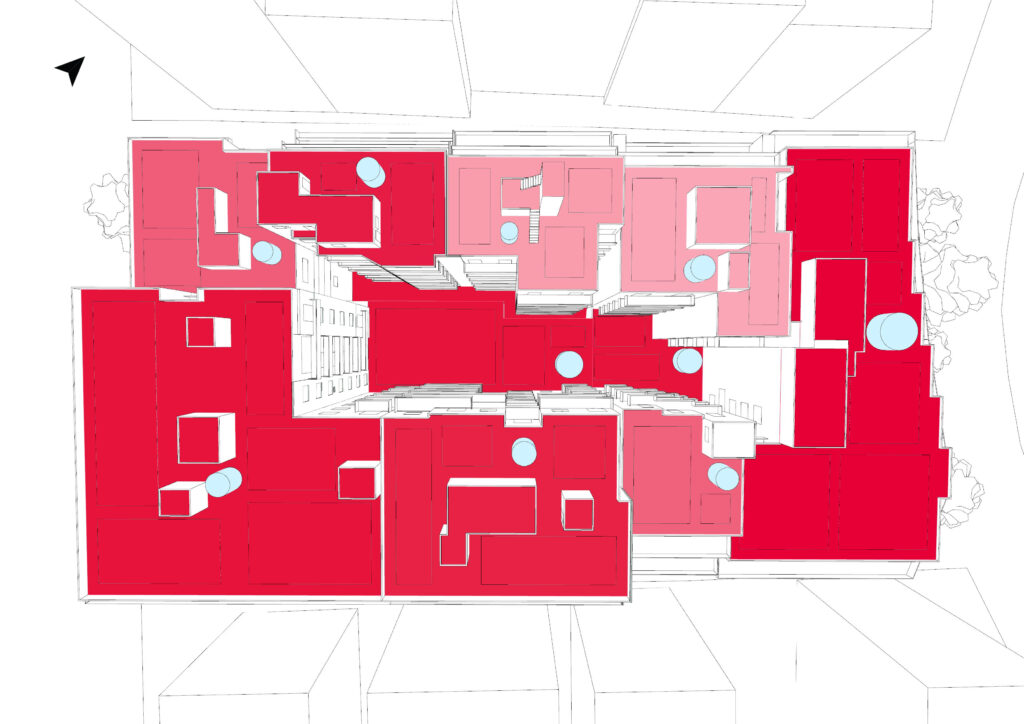
MARSH includes an extensive BMP Library featuring green roofs with varied substrate depths and plant types, green facades, stormwater harvesting cisterns, raingardens, and permeable paving. The model integrates critical simulation tools such as the Time Period Precipitation Calculator, Incident Radiation Analysis, Roof and Inner Block Runoff Estimator, and Runoff Visualization Module, enabling users to generate both quantitative outputs (e.g., irrigation potential, runoff reduction) and clear visual results.
Utilizing reliable methods like the Penman-Monteith equation for estimating irrigation demands and the SCS-CN (Soil Conservation Service Curve Number) method for runoff estimation, MARSH is tailored to provide accurate, context-specific analysis with minimal data input. A key goal of UBWARMM is to make stormwater management accessible and actionable for architectural practice by offering a user-friendly interface, light data requirements, and flexible design capabilities.
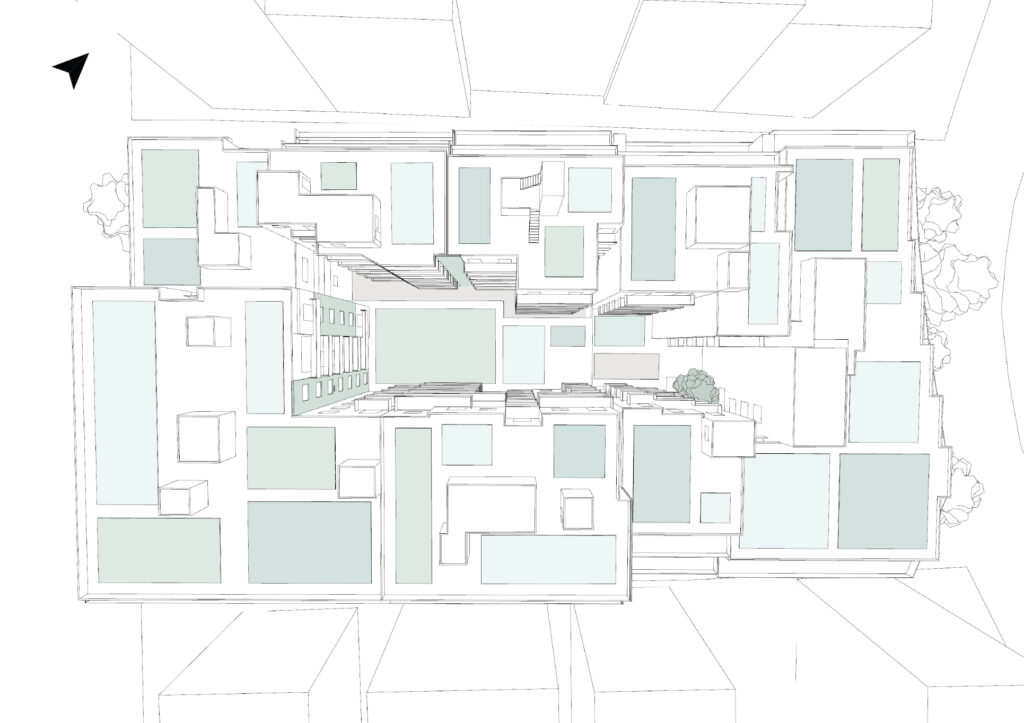
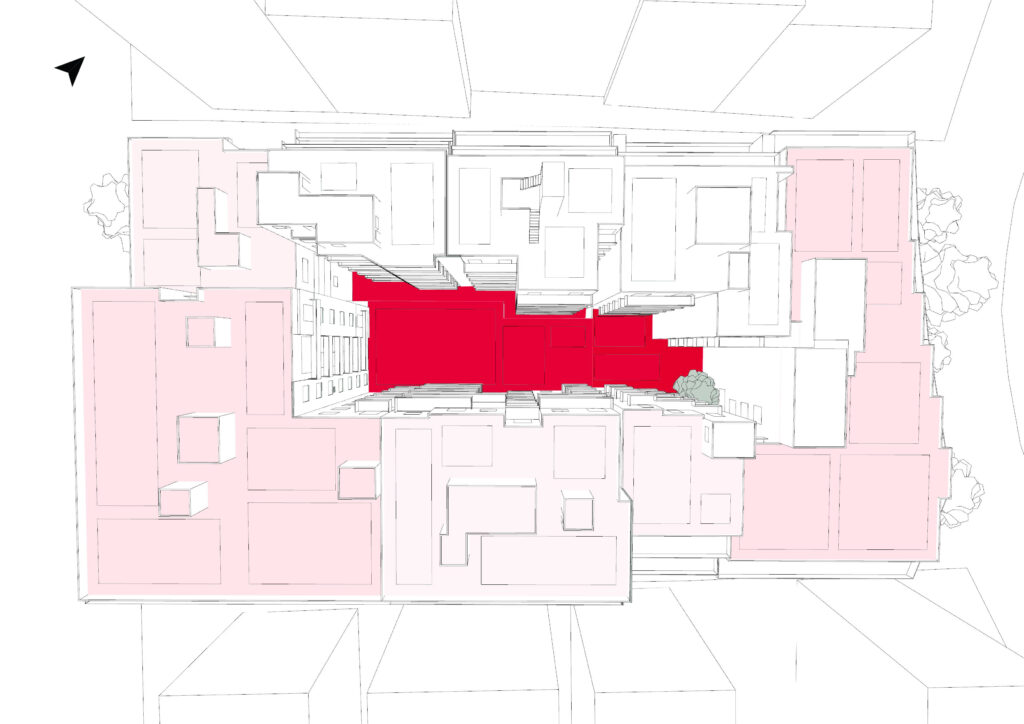
A case study conducted on an urban block in Athens, Greece served as the initial testing ground, validating the model’s efficiency, adaptability, and scalability. The findings demonstrate MARSH’s potential for both localized and broader urban applications, contributing valuable insights to the future of sustainable urban water management.
The UBWARMM project represents a significant step toward the integration of WSUD principles into mainstream architectural workflows, empowering professionals to design cities that are more resilient, climate-adaptive, and water-conscious.